Essay
In the collision theory of reaction rates, the rate constant for a bimolecular reaction can be written as k = z · p · exp 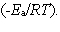 In one sentence each, clearly explain the physical meaning (interpretation) of the following three factors which appear in the above expression:
In one sentence each, clearly explain the physical meaning (interpretation) of the following three factors which appear in the above expression:
A) z
B) p
C) exp 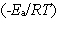
Correct Answer:

Verified
a. z is a collision rate constant, such ...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q11: The greater the energy of activation, E<sub>a</sub>,
Q32: The rate of a reaction is determined
Q71: The rate constant for a reaction is
Q80: For the reaction 3A(g) + 2B(g)
Q81: In the gas phase at 500.
Q84: Consider the following mechanism for the
Q85: Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope which decays
Q86: The decomposition of dinitrogen pentaoxide to
Q87: Based on the initial rate data
Q88: The rate constant for the reaction