Short Answer
Nitrous oxide, N2O, decomposes on metal surfaces readily at high temperatures following first-order kinetics for the equation:
2 N2O (g) 2 N2 (g) + O2 (g)
The following data are obtained for a reaction at 850°C: 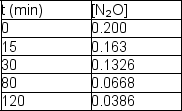 Determine the rate constant and half-life for the reaction.
Determine the rate constant and half-life for the reaction.
Correct Answer:

Verified
k = 0.0137 s-1<...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q32: The reaction of nitrogen dioxide and
Q33: Radioactive decay follows first-order kinetics. Some smoke
Q34: Ammonium cyanate undergoes rearrangement to form
Q35: For the reaction I<sup>-</sup>(aq) + OCl<sup>-</sup>(aq)
Q36: Which of the following is an
Q38: The following are initial rate data for
Q39: The three reactions below, with identical
Q40: The saturation behaviour of enzyme systems (E
Q41: Why does the rate of a reaction
Q42: For a large number of reactions in