Multiple Choice
Which should be a stronger base: ammonia, 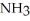 , or trifluoronitrogen,
, or trifluoronitrogen, 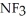 ? Why?
? Why? 
A) 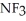 ; The fluorine atoms, being already highly electronegative, repel and tend to release the lone electron pair more easily, making it the stronger base.
; The fluorine atoms, being already highly electronegative, repel and tend to release the lone electron pair more easily, making it the stronger base.
B) 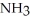 ; The fluorines have greater electronegativities and pull the lone pair electrons closer to nitrogen, thus making
; The fluorines have greater electronegativities and pull the lone pair electrons closer to nitrogen, thus making 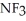 less willing to release the electron pair and thus be a weaker base.
less willing to release the electron pair and thus be a weaker base.
C) 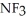 ; Ammonia tends to form a very pungent but weak base.
; Ammonia tends to form a very pungent but weak base. 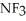 will definitely form a stronger base since the highly polar fluorines have replaced the weak hydrogens.
will definitely form a stronger base since the highly polar fluorines have replaced the weak hydrogens.
D) Neither; The nitrogens are large enough to shield the effect of either the hydrogens or fluorines from exerting any appreciable influence over the electron pair. Both molecules will have nearly identical base strength.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q37: Which of the following statements about buffers
Q38: Some molecules are able to stabilize a
Q45: Sodium hydroxide is added to a buffer
Q46: Why is the H-F bond so much
Q90: What is an acid?<br>A)anything that donates hydrogen
Q122: Which of the following statements describes a
Q140: For the following reaction,identify whether the compound
Q154: Pour vinegar onto beach sand from the
Q161: According to the following reaction,which molecule is
Q174: Why might an area with a large