Short Answer
A realtor wants to predict and compare the prices of homes in three neighboring locations. She considers the following linear models:
Model A: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β2 Age + ε
Model B: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β3 Loc1 + β4 Loc2 + ε
Model C: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β2 Age + β3 Loc1 + β4 Loc2 + ε
where,
Price = the price of a home (in $1,000s)
Size = the square footage (in sq. feet)
Loc1 = a dummy variable taking on 1 for Location 1, and 0 otherwise
Loc2 = a dummy variable taking on 1 for Location 2, and 0 otherwise
After collecting data on 52 sales and applying regression, her findings were summarized in the following table. 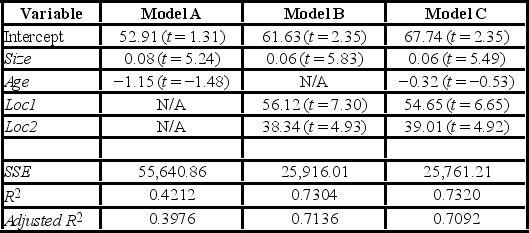 Note: The values of relevant test statistics are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Note: The values of relevant test statistics are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Using Model B, compute the test statistic for testing the joint significance of the two dummy variables Loc1 and Loc2.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q81: In the regression equation <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6618/.jpg" alt="In
Q82: Consider the model y = β<sub>0 </sub>+
Q83: The major shortcoming of the general linear
Q84: To avoid the dummy variable _, the
Q85: To examine the differences between salaries of
Q87: For the linear probability model y =
Q88: In the model y = β<sub>0</sub> +
Q89: To examine the differences between salaries of
Q90: A medical researcher is interested in assessing
Q91: Which of the following represents a logit