Multiple Choice
Select the graph of the polar equation using symmetry,zeros,maximum r-values,and any other additional points.
A) Symmetric with respect to
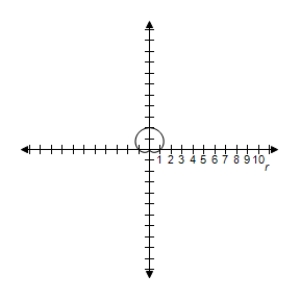
B) Symmetric with respect to 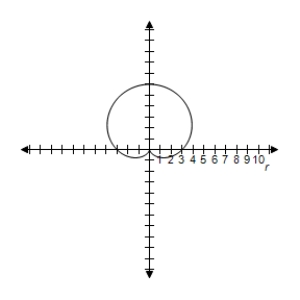
C) Symmetric with respect to 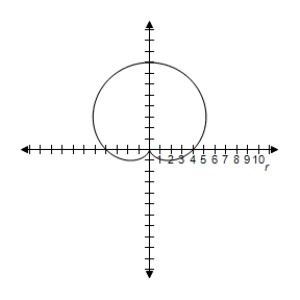
D) Symmetric with respect to 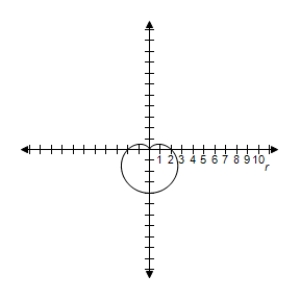
E) Symmetric with respect to 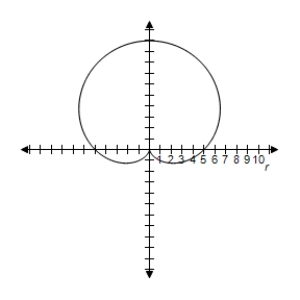
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Related Questions
Q1: Select the graph of the polar
Q2: Select the graph of the polar
Q4: Select the graph of the equation.
Q5: Select the graph of the equation.
Q6: Select the correct graph of the
Q7: Select the correct graph of the
Q8: Select the correct graph of the
Q9: Select the graph of the polar
Q10: Select the graph of the polar
Q11: Select the graph of the polar