Multiple Choice
Most effector T cells migrate out of secondary lymphoid organs and into tissues to exert their function. In which of the cases shown in Figure will the TH1 effector cell undergo long-lived interactions with its target cell, an infected macrophage? Assume all of the target cells shown below are infected with the pathogen recognized by the specific TH1 cells.
A) 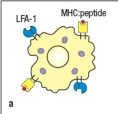
B) 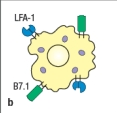
C) 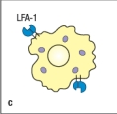
D) 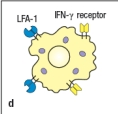
E) 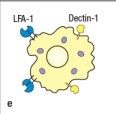
An immunological synapse forms between effector T cells and their targets to regulate signaling and to direct the release of effector molecules
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q19: Several effector T cell functions are mediated
Q20: At early timepoints following an infection,
Q21: Naive T cells scan the dendritic cells
Q22: Cytotoxic effector T cells also produce
Q23: The TNF family of cytokines and
Q25: A mouse line (called 'Wm') is
Q26: To generate a vaccine to pertussis toxin,
Q27: The entry of naive T cells from
Q28: Cytotoxic T cells are rapid killers of
Q29: Chimeric mice are generated where approximately 50%