Multiple Choice
An experiment was done to compare the effect of having a conversation via a hands-free mobile phone, having a conversation with an in-car passenger, and no distraction (baseline) on driving accuracy. Twenty participants from two different age groups (18-25 years and 26-40 years) took part. All participants in both age groups took part in all three conditions of the experiment (in counterbalanced order) , and their driving accuracy was measured by a layperson who remained unaware of the experimental hypothesis.
-Which of the following sentences is the correct interpretation of the interaction between distraction and age?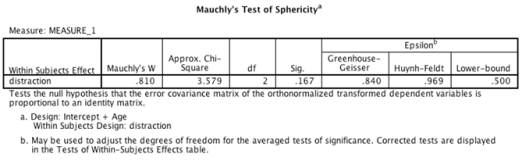
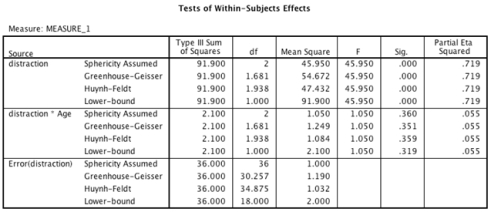
A) The age of the driver almost significantly interacted with the type of distraction, F(2, 36) = .36, p = .055.This effect tells us that profile of ratings of driving accuracy across the different types of distraction might have differed in the age groups.
B) The age of the driver did not significantly interact with the type of distraction, F(2, 36) = 1.05, p = .36.This effect tells us that profile of ratings of driving accuracy across the different types of distraction was similar for both age groups.
C) The age of the driver significantly interacted with the type of distraction, F(2, 36) = 45.95, p = .001.This effect tells us that profile of ratings of driving accuracy across the different types of distraction was different in the two age groups.
D) The interaction between age group and distraction group yielded a large effect.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: Mixed ANOVA:<br>A)Compares several means when there are
Q2: An experiment was done to compare the
Q4: Which of the following assumptions are relevant
Q5: Field and Lawson (2003) reported the
Q6: An experiment was conducted to see how
Q7: Which of the following sentences is correct?<br>A)The
Q8: An experiment was done to compare the
Q9: Field and Lawson (2003) reported the
Q10: An experiment was done to compare the
Q11: An experiment was done to compare the