Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Scenario I
Scenario I is based on fabricated data inspired by the following study:
Curry,N.A.& Kasser,T.(2005) .Can coloring mandalas reduce anxiety? Art Therapy: Journal of American Art Therapy Association,22(2) 81-85.
Effect of Coloring on Anxiety
Curry and Kasser were interested in examining whether coloring complex geometric patterns reduces anxiety.To that end,they induced anxiety in 84 undergraduate volunteers from their university.Following anxiety induction the participants were divided into two coloring conditions.To determine which condition each participant would be in the researchers put all of their names in a hat.The first name drawn was placed in group 1,the second name drawn was placed in group 2,the third name drawn was placed in group 1,and so on.Those in the complex geometric coloring condition (group 1) were given a paper with a plaid pattern or the outline of a mandala.Those in the control condition (group 2) were given a blank piece of paper.After 20 minutes of coloring all of the participants completed a self-administered State Anxiety Inventory (SAI) .Lower SAI scores indicate low levels of anxiety whereas higher SAI scores indicate high levels of anxiety.The mean SAI scores of each coloring condition were compared to determine whether the type of coloring one does affects anxiety.The results revealed that those who colored a complex geometric pattern had significantly different levels of anxiety than those who colored on a blank sheet of paper.Curry and Kasser concluded that coloring causes a change in anxiety,but only when coloring requires a certain amount of attention and focus.
Figure 1.Effect of Coloring on Anxiety
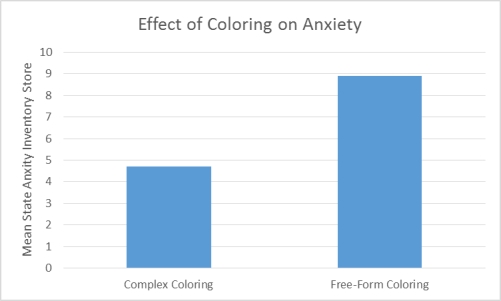
-(Scenario I) In this study,researchers identified a relationship between coloring and anxiety reduction.They were able to conclude that coloring a complex pattern causes anxiety to decrease because of:
A) covariation.
B) temporal precedence.
C) independence.
D) internal validity.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q12: (Scenario II) Which of the following is
Q31: Use the following to answer questions<br>Scenario I<br>Scenario
Q44: (Scenario II) Based on the information provided
Q45: (Scenario III) The null hypothesis of the
Q50: (Scenario III) Suppose the researchers who conducted
Q106: Use the following to answer questions<br>Scenario I<br>Scenario
Q110: Use the following to answer questions<br>Scenario III<br>Scenario
Q118: Use the following to answer questions<br>Scenario II<br>Scenario
Q136: Use the following to answer questions<br>Scenario I<br>Scenario
Q146: Use the following to answer questions<br>Scenario III<br>Scenario