Essay
The neoclassical growth model predicts that for identical savings rates and population growth rates,countries should converge to the per capita income level.This is referred to as the convergence hypothesis.One way to test for the presence of convergence is to compare the growth rates over time to the initial starting level.
(a)If you regressed the average growth rate over a time period (1960-1990)on the initial level of per capita income,what would the sign of the slope have to be to indicate this type of convergence? Explain.Would this result confirm or reject the prediction of the neoclassical growth model?
(b)The results of the regression for 104 countries were as follows: 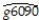 = 0.019 - 0.0006 × RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.00007,SER = 0.016,
= 0.019 - 0.0006 × RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.00007,SER = 0.016,
where g6090 is the average annual growth rate of GDP per worker for the 1960-1990 sample period,and RelProd60 is GDP per worker relative to the United States in 1960.
Interpret the results.Is there any evidence of unconditional convergence between the countries of the world? Is this result surprising? What other concept could you think about to test for convergence between countries?
(c)You decide to restrict yourself to the 24 OECD countries in the sample.This changes your regression output as follows: 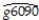 = 0.048 - 0.0404 RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.82 ,SER = 0.0046
= 0.048 - 0.0404 RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.82 ,SER = 0.0046
How does this result affect your conclusions from above?
Correct Answer:

Verified
(a)You would require a negative sign.Cou...View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q36: The reason why estimators have a sampling
Q40: (Requires Appendix material)At a recent county fair,you
Q40: Changing the units of measurement, e.g. measuring
Q41: (Requires Calculus)Consider the following model:<br>Yi = β1Xi
Q42: In a simple regression with an intercept
Q43: Interpreting the intercept in a sample regression
Q46: Assume that you have collected a sample
Q47: At the Stock and Watson (http://www.pearsonhighered.com/stock_watson)website go
Q49: In order to calculate the regression R2
Q50: In the simple linear regression model Yi