Multiple Choice
You have isolated five mutations (1 to 5) in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae that make the haploid cells unable to grow in the absence of histidine. Each haploid mutant can be mated with any of the other ones, forming diploid cells that either can (+) or cannot (-) grow in the absence of histidine, as indicated in the following complementation table. How many complementation groups do these mutations represent? Each complementation group typically corresponds to a separate gene. 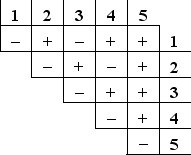
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q37: A researcher has labeled the 5? end
Q38: How is tandem affinity purification distinct from
Q39: How are antibody-producing hybridoma cell lines immortalized
Q40: In Sanger sequencing, does each labeled DNA
Q41: Indicate whether each of the following descriptions
Q43: Consider a promoter sequence with n binding
Q44: Consider a transcription regulatory protein (A) that
Q45: In sequence alignments such as those generated
Q46: Indicate whether ordinary agarose-gel electrophoresis (A), polyacrylamide-gel
Q47: You have used fluorescence-activated cell sorting to