Multiple Choice
If =1 and R=0, and if you prefer 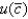 in each period 1 and 2 rather than u(c1) + u(c2) , then you are:
in each period 1 and 2 rather than u(c1) + u(c2) , then you are:
A) discounting the future.
B) risk neutral.
C) consumption smoothing.
D) satiating.
E) irrational.
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q6: Refer to the following figure when answering
Q7: Figure 16.8: Personal Savings Rates <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6622/.jpg"
Q8: Your lifetime utility is a function of:<br>A)
Q9: Consider Figure 16.7 below, which shows the
Q10: Consider consumption in two periods, <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6622/.jpg"
Q12: The consumer's lifetime utility is given as
Q13: The <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6622/.jpg" alt="The in
Q14: Behavioral economics blends economics with:<br>A) psychology.<br>B) marketing.<br>C)
Q15: As a college student, you are likely
Q16: The left-hand side of the Euler equation,