Multiple Choice
Use the following information to determine the standard enthalpy change when 1 mol of PbO(s) is formed from lead metal and oxygen gas. PbO(s) 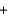 C(graphite)
C(graphite)  Pb(s)
Pb(s) 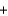 CO(g) H
CO(g) H  107 kJ
107 kJ
2C(graphite) 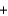 O2(g)
O2(g)  2CO(g) H 222 kJ
2CO(g) H 222 kJ
A) ( 436 kJ)
B) (436 kJ)
C) (218 kJ)
D) (329 kJ)
E) (115 kJ)
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q118: In an experiment, 10.0 g of ice
Q119: When a 13.0 g sample of NaOH(s)
Q120: The cooling system in an automobile holds
Q121: Indicate which of the following is not
Q122: Assuming that the charge of the ions
Q124: In terms of the enthalpy of formation,
Q125: A 150 g piece of iron (C<sub>P</sub>
Q126: Using the following data for water, determine
Q127: At a certain elevation, the boiling point
Q128: A 15 g piece of iron (C<sub>P</sub>