Multiple Choice
For which reaction below does the enthalpy change under standard conditions correspond to a standard enthalpy of formation?
A) 2H2(g) 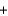 C(s)
C(s)  CH4(g)
CH4(g)
B) CO2(g) 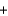 C(s)
C(s)  2CO(g)
2CO(g)
C) 2NO2(g)  N2O4(g)
N2O4(g)
D) CO(g) 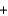 H2O(g)
H2O(g)  CO2(g)
CO2(g) 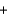 H2(g)
H2(g)
E) CO2(g) 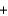 H2(g)
H2(g)  CO(g)
CO(g) 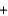 H2O(g)
H2O(g)
Correct Answer:

Verified
Correct Answer:
Verified
Related Questions
Q126: Using the following data for water, determine
Q127: At a certain elevation, the boiling point
Q128: A 15 g piece of iron (C<sub>P</sub>
Q129: Which statement A-D about a system and
Q130: Use the following information to determine the
Q132: Which of the following fuels has the
Q133: Steam in a cylinder is compressed by
Q134: Using the data shown below for water,
Q135: To cool your 250 mL of coffee
Q136: Determine the standard enthalpy of formation for